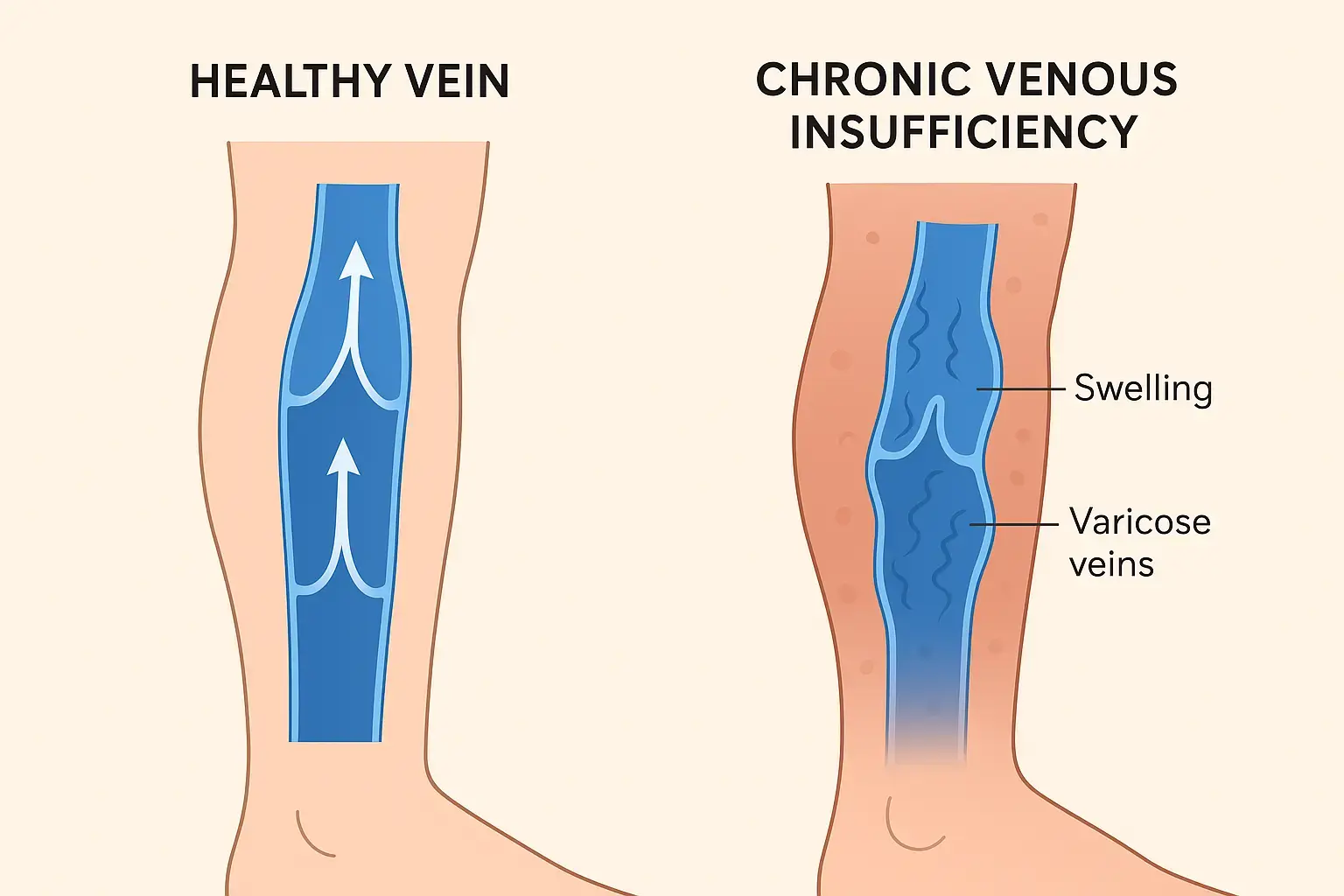
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) is a condition where your leg veins become damaged and struggle to send blood back up to your heart. This leads to blood pooling in the lower limbs, causing swelling, pain, and visible varicose veins. If left untreated, it can progress to skin changes, ulcers, and reduced quality of life.
What Is Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
Chronic Venous Insufficiency is a circulatory disorder that occurs when the valves in the veins of the legs become weak or damaged, allowing blood to flow backward and pool in the lower extremities. This backward flow, called venous reflux, increases pressure in the veins and leads to various symptoms.
How It Happens
Veins in your legs have one-way valves that push blood toward the heart. When these valves become incompetent due to age, obesity, pregnancy, or prolonged standing, the blood flows backward and collects in the legs.
Symptoms of Chronic Venous Insufficiency
- Swelling in the lower legs or ankles (especially after standing)
- Aching or cramping pain in the legs
- Itchy, flaky, or leathery skin on the legs
- Visible varicose or spider veins
- Skin discoloration near the ankles
- Venous ulcers (open sores that heal slowly)
What Is Stage 3 Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
CVI is often classified using the CEAP Classification, which ranges from C0 (no symptoms) to C6 (ulcers).
Stage 3 CVI (C3):
Clinical Sign: Leg edema (swelling) without skin changes.
This is the intermediate stage, indicating significant venous dysfunction but no ulceration yet.
What Causes Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
What Is the Most Common Cause of Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
The leading cause is valve damage due to deep vein thrombosis (DVT), also known as post-thrombotic syndrome. Other contributing factors include:
- Genetics (family history of varicose veins)
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Prolonged standing or sitting
- Smoking
- Hormonal therapies (like birth control)
Risk Factors for CVI
- Age over 50
- Female gender
- Jobs requiring long standing
- History of blood clots
- Inactivity
How Do You Fix Venous Insufficiency?
Treatment depends on the severity. Early intervention helps prevent complications.
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Elevate your legs above heart level
- Avoid long periods of standing or sitting
- Exercise regularly
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid tight clothing
2. Compression Therapy
Wearing compression stockings is the first-line treatment. They:
- Improve blood flow
- Reduce swelling
- Relieve symptoms
3. Medications
- Venoactive drugs (e.g., micronized purified flavonoid fraction)
- Diuretics (short-term use for swelling)
- Topical/oral antibiotics (for infections)
4. Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA)
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
- Vein stripping (rarely used now)
What Is the Best Supplement for Venous Insufficiency?
Some supplements can support vein health and reduce inflammation.
Top Supplements for CVI:
- Horse Chestnut Extract – reduces swelling and improves venous tone
- Diosmin and Hesperidin – support vein elasticity
- Gotu Kola (Centella Asiatica) – enhances collagen synthesis
- Butcher’s Broom – reduces venous pooling
- Pycnogenol – antioxidant that strengthens blood vessels
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting supplements.
Diagnosis of Chronic Venous Insufficiency
- Duplex Ultrasound
- Venography
- Photoplethysmography
Long-Term Complications
- Lipodermatosclerosis
- Stasis dermatitis
- Venous ulcers
- Reduced mobility and chronic pain
- Increased risk of infections
Prevention Tips
- Don’t sit or stand too long
- Elevate your legs
- Exercise daily
- Maintain a healthy BMI
- Wear compression garments
- Avoid hot baths or saunas
FAQs (People Also Ask)
How do you fix venous insufficiency?
By combining compression therapy, lifestyle changes, supplements, and minimally invasive procedures like laser or radiofrequency ablation, you can manage and sometimes reverse the symptoms.
What is the most common cause of chronic venous insufficiency?
Previous deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is the most common cause, followed by genetic weakness of the vein walls and valves.
What is the best supplement for venous insufficiency?
Horse Chestnut Extract, Diosmin, and Gotu Kola are the top choices, backed by research for reducing swelling and improving vein tone.
What is stage 3 chronic venous insufficiency?
Stage 3 is characterized by visible leg swelling without skin damage. It's a moderate phase of the condition that often responds well to compression and medical intervention.
Final Thoughts
Chronic Venous Insufficiency affects millions and can significantly impact daily life if untreated. Fortunately, early intervention, proper diagnosis, supplements, and lifestyle changes can help manage and even reverse its progression.
If you're experiencing leg pain, swelling, or visible veins, consult a vein specialist or vascular surgeon to explore your treatment options.
References
- Mayo Clinic – Varicose veins and CVI overview
- NIH – Chronic Venous Insufficiency Clinical Review
- Journal of Vascular Surgery – Clinical updates on venous disorders
- PubMed – Search "Chronic Venous Insufficiency" for peer-reviewed studies
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *












-150x150.webp)
